Approach to Thoracic Ultrasound
Thoracic ultrasound
-
Fluid in chest cavity
- Pleural effusion
- Hemothorax – adjunct to FAST
- Pneumothorax
-
Interstitial fluid
- “alveolar interstitial syndrome” (AIS)
- Pulmonary edema
Narration
So thoracic US can be a stand alone examination or it can be integrated into various examinations such as the FAST exam or the BLUE protocol for shortness of breath. It’s particularly good for finding pleural effusions in the inferior thoracic spaces which can also be a soon to be hemothorax if it’s a new effusion in a traumatic exam, such as fast exam. It can also be helpful for finding pneumothorax, either traumatic or spontaneous, and interstitial fluid, such as alveolar interstitial syndrome, fluid that is typically from pulmonary edema or congestive heart failure in the acute setting.
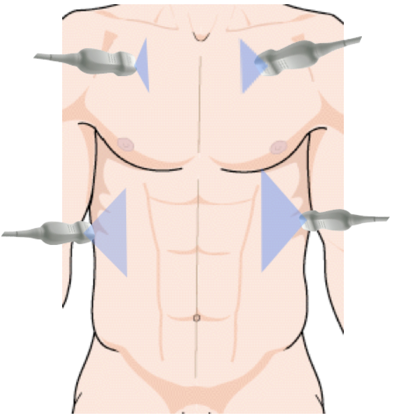
Probe selection
- Curvilinear – inferior thoracic spaces
- Linear – anterior thoracic line
- Phased array – can be for either
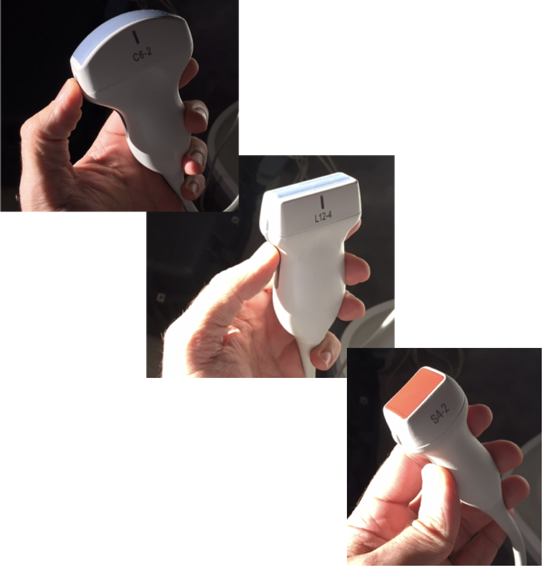

Narration
When we perform thoracic US we may use any of the three probes shown here. Most typically for evaluation of the inferior thoracic spaces we may start with the curvilinear probe, although the phased array probe is very good for getting in between rib spaces and interrogating the lower thoracic space. When we are looking at the anterior thoracic line, the linear probe may give the most detail, although we can use the phased array probe to look for artifact, such as b lines that we’ll talk about.
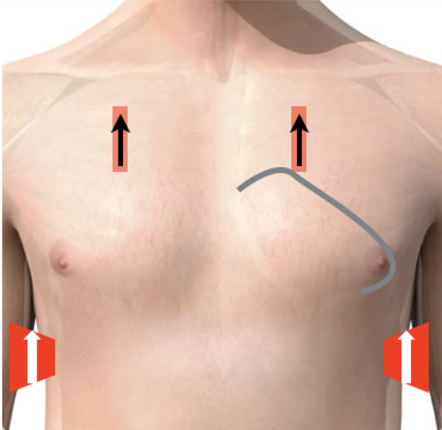
Narration
So this shows the basic thoracic windows, the anterior spaces are superior and we’re really looking at the pleural line for sliding and pathology such as B lines. The inferior thoracic spaces you’ll recognize from the exam we did such as the coronal view of the liver and the kidney but you just look a little more superiorly above the diaphragm to see if there is fluid above the diaphragm which would represent a pleural effusion or hemothorax in trauma.